What is Sickle cell disease ?
Sickle cell disease is a group of disorders that affects molecule in red blood cells (hemoglobin) that delivers oxygen to cells throughout the body. Person with this disorder have typical hemoglobin molecules called hemoglobin S, which can distort red blood cells into a sickle, or crescent, shape.
What are the symptoms of sickle cell disease?
Symptoms of sickle cell disease usually begin in early childhood. Characteristic features of this disorder include Anemia (low number of red blood cells), repeated infections, and periodic episodes of pain. The severity of symptoms varies from person to person.
The sickle-shaped cells are not flexible and cannot change shape easily. Many of them burst apart as they move through blood vessels. Sickle cells usually last only for 10 to 20 days, instead of the normal 90 to 120 days. Body may have trouble making enough new cells to replace the ones that is lost.
The signs of sickle cell disease are caused by the sick ling of red blood cells (RBC). When red blood cells sickle, they break down prematurely, which can lead to anemia. Anemia can cause shortness of breath, fatigue, and delayed growth and development in children. The rapid breakdown of red blood cells may also cause yellowing of the eyes and skin, which are signs of jaundice. A particularly serious complication of sickle cell disease is high blood pressure in the blood vessels that supply the lungs (pulmonary hypertension). Pulmonary hypertension occurs in about one-third of adults with sickle cell disease and can lead to heart failure.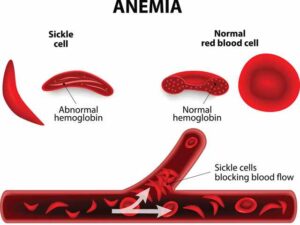
Types of Sickle Cell Disease
Following are the most common types of SCD:
HbSS
People who have this form of SCD inherit two sickle cell genes (“S”), one from each parent. This is commonly called sickle cell anemia and is usually the most severe form of the disease.
HbSC
People who have this form of SCD inherit a sickle cell gene (“S”) from one parent and from the other parent a gene for abnormal hemoglobin called “C”. Hemoglobin is a protein that allows red blood cells to carry oxygen to all parts of the body. This is usually a milder form of SCD.
HbS beta thalassemia
People who have this form of SCD inherit one sickle cell gene (“S”) from one parent and one gene for beta thalassemia, another type of anemia, from the other parent. There are two types of beta thalassemia: “0” and “+”. Those with HbS beta 0-thalassemia usually have a severe form of SCD. People with HbS beta +-thalassemia tend to have a milder form of SCD.
There also are a few rare types of SCD:
HbSD, HbSE, and HbSO
People who have these forms of SCD inherit one sickle cell gene (“S”) and one gene from an abnormal type of hemoglobin (“D”, “E”, or “O”). Hemoglobin is a protein that allows red blood cells to carry oxygen to all parts of the body. The severity of these rarer types of SCD varies.
Sickle Cell Trait (SCT)
HbAS
People who have SCT inherit one sickle cell gene (“S”) from one parent and one normal gene (“A”) from the other parent. This is called sickle cell trait (SCT). People with SCT usually do not have any of the signs of the disease and live a normal life, but they can pass the trait on to their children. Additionally, there are a few, uncommon health problems that may potentially be related to sickle cell trait
Signs and Symptoms of Sickle Cell diseases
Signs and symptoms of sickle cell disease can be mild or severe enough to require frequent hospitalizations. They may include:
- Anemia (looking pale)
- Dark urine
- Yellow eyes
- Painful swelling of hands and feet
- Frequent pain episodes
- Stunted growth
- Stroke
Diagnosis
SCD is diagnosed with a simple blood test. It most often is found at birth during routine newborn screening tests at the hospital. In addition, SCD can be diagnosed before birth.
- Blood counts can reveal an abnormal Hb level in the range of 6 to 8 grams per deciliter.
- Blood films may show RBCs that appear as irregularly contracted cells.
- Sickle solubility tests look for the presence of Hb S.
Tests commonly performed to diagnose and monitor patients with sickle cell anemia include:
- Blood oxygen saturation
- Complete blood count (CBC)
- Bilirubin
- Hemoglobinopathy (Hb) evaluation: There are several methods of evaluating the type and relative amounts of various normal and abnormal hemoglobin types. These methods typically separate the different types of hemoglobin that are present so that they can be identified and quantified. They include:
- Hemoglobin electrophoresis traditionally used to confirm the diagnosis of sickle cell disease. It measures the different types of hemoglobin in the blood
- Hemoglobin fractionation by HPLC, the most frequently used method to screen for hemoglobin variants, including Hb S
- DNA Analysis: Test to investigate alterations and mutations in the genes that produce hemoglobin components. It may be performed to determine whether someone has one or two copies of the Hb S mutation or has two different mutations in hemoglobin genes (e.g., Hb S and Hb C).
- Blood smear (also called peripheral smear and manual differential): The number and type of red blood cells are evaluated to see if they are normal. Sickle-shaped RBCs may be seen on the blood smear.
- Iron studies: These may include: iron, ferritin, UIBC, TIBC, and transferrin saturation. These tests measure different aspects of the body’s iron storage and usage. They are ordered to help determine whether someone has an iron deficiency anemia or an excess amount of iron.
- Serum potassium
- Sickle cell test
Treatment of Sickle Cell Disease Treatment
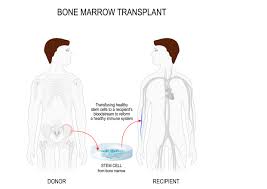
The only cure for SCD is Steam Cell transplantation. Because these transplants are risky and can have serious side effects, they are usually only used in children with severe SCD. For the transplant to work, the bone marrow must be a close match. Usually, the best donor is a brother or sister.
There are treatments that can help relieve symptoms, lessen complications, and prolong life:
- Antibiotics to try to prevent infections in younger children
- Pain relievers for acute or chronic pain
- Hydroxyurea, a medicine that has been shown to reduce or prevent several SCD complications. It increases the amount of fetal hemoglobin in the blood. This medicine is not safe during pregnancy.
- Childhood immunizations to prevent infections
- Blood transfusions for severe anemia. If one has some serious complications, such as a stroke,
transfusions are required to prevent more complications.
Best Sickle Cell Disease treatment in India
Best Sickle cell disease treatment in India have mastered the technology for isolating maximum number of viable stem cells allogenically with the matched donor to treat various patients with SCD. There are various super specialty hospitals with the excellent, well equipped state of the art facility to isolate process and enrich the viable number of stem cells, which can be re infused back into the patient’s body. Generally, these cells are administered through any one of the below mentioned methods depending upon expert’s advice:
- Local Administration:-Through this mode, cell are infused directly at the targeted site of injury. Thus, in case of cancer of particular organ, cells can be directly infused at the targeted site after prescribed chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy.
- Intravenous Administration:- Through this mode, cells are infused through the veins to expand blood volumes in the central nervous system, to ensure that the maximum number of cells are reaching to the targeted area.
Thus, once infused back in the body, these cells are known to revamp the cellular system in bone marrow as well as in damaged organs. Thus, the recovery period after the transplant, is found to be between 1 to 2 months; depending upon the patient’s health, age and will power.
The collected data from various clinical trials has suggested that 85 out of 100 children have restructured body’s natural defense mechanism completely after stem cells treatment.
What is the cost of Sickle Cell disease treatment ?
- Primary cost would be the cost of the sickle cell transplant in India which will cover the cost of the preliminary conditioning regimes, cost of the actual procedure of transplant and the initial follow up after the procedure. This would range between 28K to 40K USD in India.
- The second cost involved is for treating the complications or side effects developed as a result of the sickle cell anemia condition. This would vary from person to person depending on the side effect that the person develops.
Even though best sickle cell disease treatment in India modalities include medication, vaccinations or blood transfusion also, the most effective and permanent solution is a considered to be the sickle cell disease transplant, especially when it is undertaken in children. Hence the primary cost becomes valid for any person looking for a more permanent treatment for sickle cell disease. Transplanting healthy bone marrow to the bloodstream of affected person helps to develop new healthy bone marrow cells which are responsible for developing the new healthy red blood cells. Since the condition is more of a genetic nature autologous transplant is carried out. This is the type of transplant wherein the healthy stem cells from a donor is harvested to plant in the recipient who is suffering from the condition. These new cells start multiplying rapidly to replace/replenish the sickle cells in the body
The cost of best sickle cell disease treatment in India mainly depends on the source of the donor providing the healthy sickle cells. The basic criteria for identifying a potential donor is the HLA matching. First preference is for a donor with an HLA matching from the immediate family. This helps to reduce the risk of rejection. In case a donor is not identified from the family then the next choice is the bone marrow registries worldwide. In India in the absence of a matching donor from the family, the availability of HLA matching donor is first checked in the local bone marrow registry. In case the HLA matching donor has to be sourced from a worldwide registry outside India then the cost of the procedure could move upwards to 60K USD. For more information related to Best Sickle Cell disease treatment in India . Click Here…
Related Article –
- Best Bone marrow transplant hospitals in India
- Cost of Bone marrow transplant in India
- Experience of Mr. John of Kenya after a successful stem cell transplant for Multiple Myeloma in India